Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI of the Brain and Spine. Gradient echo GRE Steady-state free precession SSFP Echo-planar imaging EPI To eliminate patient motion which will overwhelm the diffusion phenomenon we must use the fastest imaging sequence possible - echo-planar.
Gre V Se Questions And Answers In Mri

High Diagnostic Value Of Gradient Echo Sequence In Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis
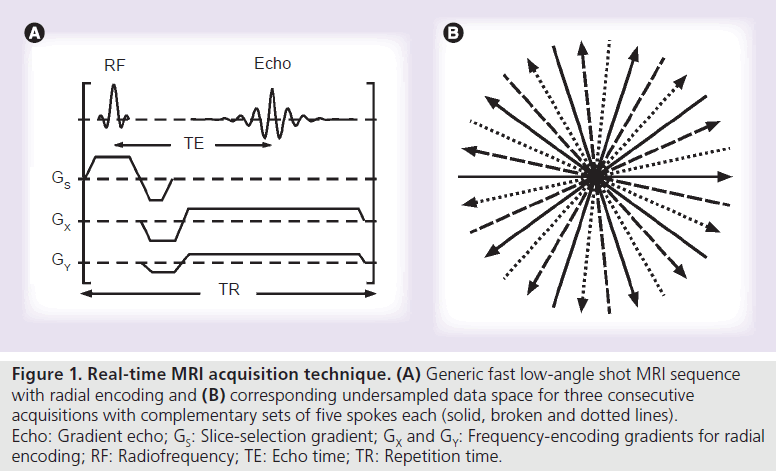
Real Time Mri Recent Advances Using Radial Flash
With a gradient echo pulse sequence and approximately as far as 14 mm from the devices when imaged with a spin echo pulse sequence in a 3 T MRI system.

Gradient echo sequence mri. Inversion recovery sequence with a long inversion time TI of 2000-2500 is used for fluid suppression. Present the sequence acceleration techniques in spin echo Examine the effect of inversion-recovery on contrast and its applications Define the relationship between TR flip angle and longitudinal magnetization in gradient echo. These are T1 weighted gradient-echo sequences.
The gradient echo sequence differs from the spin echo sequence in regard to. The T1 relaxation time also known as the spin-lattice relaxation time is a measure of how quickly the net magnetization vector NMV recovers to its ground state in the direction of B o. The specific parameters for any given study varies from one manufacturer to another and from one imaging center to another.
This sequence is similar to the spin-echo sequence except that the initial RF pulse is less than 90 and there is no 180 RF pulse. In nonclinical testing the image artifact caused by the device extends approximately 13 mm from the stent when imaged with a gradient echo pulse sequence and a 3 Tesla MRI system. In FLAIR the signal from fluid is nullified by using a long effective echo time and long inversion time.
A flip angle lower than 90 partial flip angle decreases the amount of magnetization tipped into the transverse plane. Spoiled gradient echo Figure 5 - Balanced SSFP sequence is very susceptible to artefacts caused by ferromagnetic metals. Please refer to MRI manufacturers published value and location of the peak SG.
MRI ADDITIONAL INFORMATION The highest spatial gradient magnetic field is commonly located off-axis at a side wall and near the opening of the bore of the scanner. Of the echo in time. Viability study delayed also known as myocardial enhancement study These are T1 weighted gradient-echo sequences.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI Important Safety Information. Optimization of MR imaging parameters to compensate for the presence of the device may. This is normally achieved by using a long repetition time TR 2000-6000ms and a long echo time TE 100-150ms.
If there is a hypoenhanced area this implies a zone of myocardial infarction that is non-viable. The echo is measured from. This method calculates a field map from a double-echo gradient echo sequence.
Echo planar images are subject to severe field inhomogeneity artifacts limiting usefulness near air or bone interfaces. For MRI a time-varying radiofrequency RF field commonly referred to as B1 must be first transmitted into the spin system near the Larmor frequencyIn addition to having specific frequency the B1 field must also be applied perpendicular to the main magnetic field BoThe B1 field is produced by driving electrical currents through specialized RF-transmit coils. The field map is calculated by taking the difference between the two phase images and dividing that by the echo time difference.
The lumen is partially to fully obscured under these conditions. A spoiled gradient echo sequence can also be used to acquire cine images which is relatively less susceptible to such artefacts and. ACME Overthruster MRI SAFETY INFORMATION Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that the ACME Overthruster is MR Conditional.
This gradient modifies the spin phase in a spatially dependent manner so that at the end of the gradient the signal will be completely canceled because the coherence between the spins will be completely destroyed. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance NMR and magnetic resonance imaging MRI make use of this effect. Gradient-recalled-echo pulse sequence.
Signal dephasing and rephasing by means of gradient pulses results in formation of a gradient echo which is used to produce T1- or T2-weighted images. In magnetic resonance a spin echo is the refocusing of spin magnetisation by a pulse of resonant electromagnetic radiation. FLAIR is another variation of the inversion recovery sequence.
Specialised MRI images - such as STIR FLAIR Gradient echo or T2 STAR - T2 and DWI diffusion-weighted images - can be produced in order to answer specific clinical questions. The maximum image artifact produced by a MR gradient echo pulse sequence was a moderate localized signal void in size and shape of the implant. Maximum spatial gradient field of 300 Gausscm 3 Tm Maximum switched gradient slew rate per axis of 200 mTmms.
MR image quality may be compromised if the area of interest is in the same area or relatively close to the position of these devices. The difference in phase between the two images is proportional to the difference in echo times and the B0 inhomogeneity. Advanced MRI assessment of non-enhancing peritumoral signal abnormality in brain lesions.
Listed in the table below are the most common acquisition parameters for commonly used MRI pulse sequences in msec. The NMR signal observed following an initial excitation pulse decays with time due to both spin relaxation and any inhomogeneous effects which. The artifact does obscure the device lumen.
A T2-weighted sequence produces T2 contrast mainly by de-emphasizing the T1 contributions. Three sets of gradient coils are used in nearly all MR systems. CERTAS Plus Valve when imaged with a gradient echo pulse sequence and a 3T MRI System.
As with a real MR sequence the phase encoding gradient is turned on and off first then frequency encoding is applied. The gradient echo sequence is characterized by a single excitation followed by a gradient applied along the reading axis called the dephasing gradient. Setting up the.
Axial sagittal and coronal see the example image below. The x- y- and z-gradientsEach coil set is driven by an independent power amplifier and creates a gradient field whose z-component varies linearly along the x- y- and z-directions respectivelyThe design of the z-gradients is usually based on circular Maxwell coils while the transverse x- and y- gradients typically. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is one of the most commonly used tests in neurology and neurosurgeryMRI provides exquisite detail of brain spinal cord and vascular anatomy and has the advantage of being able to visualize anatomy in all three planes.
Gradient echo pulse sequence and a 15 Tesla MRI system 31. The flip angle usually below 90 the absence of a 180 RF rephasing pulse. For a general introduction to these sequences please refer to MRI sequences basic.
This image was acquired using a steady state gradient echo sequence balanced Fast Field Echo with a 256 x 256 image grid from 192 phase-encodings. A magnetic resonance imaging sequence produces signal from all the tissue in the scanner. Image acquisition is performed 3 minutes after gadolinium contrast administration.
T1 weighting occurs in a short TR spin echo sequence because of incomplete recovery of longitudinal magnetization. Nevertheless this k -space tutorial permits one to load any image and apply every parameter or function of this educational environment to any image selected by the user either in DICOM digital imaging and.

Gradient Echo Mri Neurology
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Steady State Echo Mri Shark
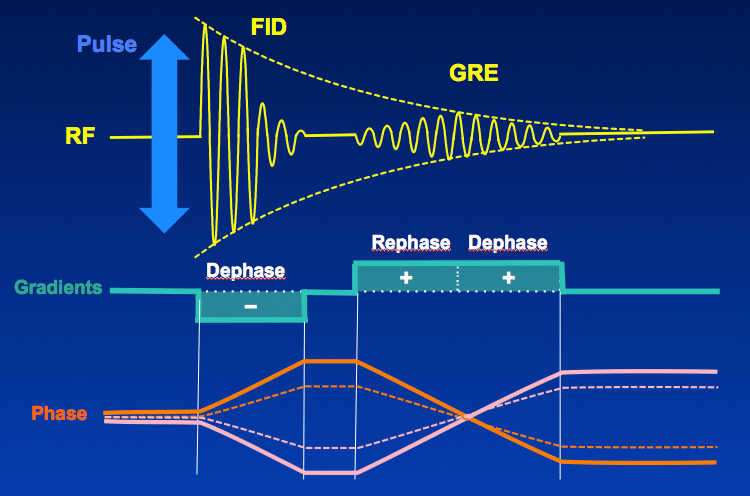
Gradient Echo Gre Questions And Answers In Mri

Gradient Recalled Echo Sequence Radiology Cafe
Spoiling Questions And Answers In Mri

Mri Sequences Classification

Magnetic Resonance Imaging Mri Of The Brain Gradient Echo Sequence Download Scientific Diagram
